Appendixes
Shortcuts
Connection Panel
|
Esc |
Closes the window. |
|
Ctrl+Enter |
Opens the Configuration Panel (main interface). |
|
Arrow keys |
The Up and Down arrow keys are used to select a VPN connection. |
|
Ctrl+O |
Opens the selected VPN connection. |
|
Ctrl+W |
Closes the selected VPN connection. |
VPN configuration tree
|
F2 |
Used to edit the name of the selected. |
|
Del |
Deletes a selected phase, following confirmation by the user. If the actual configuration is selected (root of the tree), the software asks whether a full reset of the configuration should be performed. |
|
Ctrl+O |
Opens the corresponding VPN tunnel if a Child SA is selected. |
|
Ctrl+W |
Closes the corresponding VPN tunnel if a Child SA is selected. |
|
Ctrl+C |
Copies the selected phase to the clipboard. |
|
Ctrl+V |
Pastes (adds) the phase that has previously been copied to the clipboard. |
|
Ctrl+N |
If the VPN configuration is selected, creates a new IKE Auth. If an IKE Auth is selected, creates a Child SA. |
|
Ctrl+S |
Saves the VPN configuration. |
Configuration Panel
|
Ctrl+Enter |
Switches to the Connection Panel. |
|
Ctrl+D |
Opens the Console window with VPN traces. |
|
Ctrl+Alt+R |
Restarts the IKE service. |
|
Ctrl+Alt+T |
Enables trace mode (log generation). |
|
Ctrl+S |
Saves the VPN configuration. |
Administrator logs
|
ID Log define |
ID Log value |
Severity |
Log string |
|---|---|---|---|
|
LOGID_STARTERINIT |
1001 |
Notice |
Starter service is started. |
|
LOGID_VPNCONFSTARTING |
2001 |
Notice |
GUI is starting. |
|
LOGID_VPNCONFSTOPPED |
2002 |
Notice |
GUI has closed. |
|
LOGID_TGBIKESTARTED |
3001 |
Notice |
IKE has started (status %d). |
|
LOGID_TGBIKESTOPPED |
3002 |
Notice |
IKE has stopped. |
|
LOGID_TUNNELOPEN |
3004 |
Info |
Tunnel %s is asked to open. |
|
LOGID_VPNCONFCRASHED |
2003 |
Notice |
GUI crashed (state %d). |
|
LOGID_TGBIKECRASHED |
3003 |
Notice |
IKE crashed (state %d). |
|
LOGID_STARTERSTOP |
1002 |
Notice |
Starter service is stopped. |
|
LOGID_RESETIKE |
2007 |
Warning |
IKE is asked to reset. |
|
LOGID_VPNCONFSTARTED |
2008 |
Notice |
GUI has started from user %s. |
|
LOGID_VPNCONFSTOPPING |
2009 |
Notice |
GUI is stopping from user %s. |
|
LOGID_VPNCONFLOADERROR |
2010 |
Error |
Configuration couldn’t load (reason: %s). |
|
LOGID_VPNCONFOPENTUNNEL |
2011 |
Info |
GUI opens tunnel (source: %s). |
|
LOGID_VPNCONFCLOSETUNNEL |
2012 |
Info |
GUI closes tunnel (source: %s). |
|
LOGID_VPNCONFSAVE |
2013 |
Notice |
New configuration is saved. |
|
LOGID_VPNCONFIMPORT |
2014 |
Info |
%s has been imported. |
|
LOGID_VPNCONFIMPORTERR |
2015 |
Error |
%s could not be imported (status %d). |
|
LOGID_VPNCONFEXPORT |
2016 |
Info |
%s has been exported. |
|
LOGID_TOKENINSERT |
2017 |
Info |
Token %s has been inserted. |
|
LOGID_TOKENEXTRACT |
2018 |
Info |
Token %s has been extracted. |
|
LOGID_USBINSERT |
2019 |
Info |
USB Key has been inserted. |
|
LOGID_USBEXTRACT |
2020 |
Info |
USB Key has been extracted. |
|
LOGID_INSTALLATION |
2021 |
Info |
VPN running for the 1st time. |
|
LOGID_UPDATE |
2022 |
Info |
VPN software has been updated to version %s. |
|
LOGID_VERSION |
2023 |
Info |
VPN Version is %s. |
|
LOGID_GINASTARTED |
4001 |
Notice |
GINA has started. |
|
LOGID_GINASTOPPING |
4002 |
Notice |
GINA is stopping. |
|
LOGID_GINAOPENTUNNEL |
4003 |
Info |
GINA opens tunnel (source: %s). |
|
LOGID_GINACLOSETUNNEL |
4004 |
Info |
GINA closes tunnel (source: %s). |
|
LOGID_TUNNELAUTH_OK |
3005 |
Info |
Tunnel authentication Ok (%s). |
|
LOGID_TUNNELTRAFIC_OK |
3006 |
Info |
Tunnel %s Ok |
|
LOGID_TUNNELAUTH_NOK |
3007 |
Error |
Tunnel authentication failed (reason %d). |
|
LOGID_TUNNELTRAFIC_NOK |
3008 |
Error |
Tunnel %s failed (reason %d). |
|
LOGID_AUTHREKEYING |
3009 |
Info |
Tunnel %s initiated rekey (source %d). |
|
LOGID_AUTHREKEYED |
3010 |
Info |
Tunnel %s rekeyed. |
|
LOGID_TUNNELREKEYING |
3011 |
Info |
Tunnel %s initiated rekey (source %d). |
|
LOGID_TUNNELREKEYED |
3012 |
Info |
Tunnel %s rekeyed. |
|
LOGID_PINCODE |
3013 |
Notice/Error |
Pin code is entered (status %d). |
|
LOGID_DRIVERNOK |
3014 |
Critical |
Driver could not be loaded (status %d). |
|
LOGID_IKEEXT_STOP |
1003 |
Warning |
IKEEXT service is stopped. |
|
LOGID_IKEEXT_RESTART |
1004 |
Notice |
IKEEXT service is restarted. |
|
LOGID_IKEEXT_ERROR |
1005 |
Critical |
IKEEXT could not be stopped (status %d). |
|
SYSTEMLOGID_VIRTIFOK |
3015 |
Info |
Virtual interface created successfully (instance %d). |
|
SYSTEMLOGID_VIRTIFNOK |
3016 |
Error |
Virtual interface could not be created (error %d). |
|
LOGID_TUNNELCLOSED |
3017 |
Notice |
%s tunnel successfully closed (%d min). |
|
LOGID_TUNNELCLOSED_ERR |
3018 |
Error |
%s tunnel closed unexpectedly (%d). |
|
LOGID_CERTERROR |
3019 |
Error |
Error %d when handling certificate %s. |
TrustedConnect Panel diagnostics
The TrustedConnect Panel informs the user of any issues that may have occurred while establishing the VPN connection by displaying an error code.
These error codes, their diagnosis and possible solutions are detailed below. This list allows administrators to find possible answers to any issues that users may encounter and report.
|
Code |
Diagnosis |
Solution |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
VPN configuration issue VPN connection not found in configuration |
|
|
1 |
Issue with a certificate The VPN configuration uses a certificate whose private key cannot be found. |
|
|
3 |
Configuration issue The message No proposal chosen has been received during an IKE exchange: the cryptographic algorithm suite configured for the IKE_SA_INIT sequence does not match the one configured on the gateway. |
|
|
4 |
Configuration issue The message “No proposal chosen” has been received during an IKE exchange: the cryptographic algorithm suite of the ESP protocol does not match the one configured on the gateway. |
|
|
5 |
Cannot access gateway The gateway address (“Remote Router Address”) specified in the VPN configuration is not reachable. If it is an IP address, it cannot be found or cannot be reached. If it is a DNS address it may be inaccessible, indefinite, or cannot be resolved. |
|
|
6 |
Configuration issue The message Remote ID other than expected has been received. This means that the value of the Remote ID does not match the value expected by the remote VPN gateway. |
|
|
7 |
Gateway certificate Checking the certificate chain of the certificate received from the VPN gateway is enabled. The gateway certificate chain could not be validated. |
|
|
9 |
No response from gateway The VPN Client has abandoned the connection, most often after several connection attempts. |
|
|
10 |
Authentication issue The gateway has declined the user’s authentication credentials. |
|
|
13 |
Configuration issue An error occurred while establishing the VPN connection. Establishing the VPN connection has been abandoned. |
|
|
14 |
Network configuration An error occurred while creating the virtual interface used for the VPN connection. |
|
|
15 |
Network configuration The virtual IP address assigned during the VPN connection already exists on one of the workstation’s interfaces. |
|
|
16 |
Network configuration An error occurred while creating the virtual interface used for the VPN connection. |
|
|
24 |
Configuration issue The gateway did not accept the cryptographic algorithm suite provided by the VPN Client. |
|
|
25 |
Configuration issue The gateway did not accept the remote network configured in the VPN Client or the virtual IP address provided by the VPN Client. |
|
|
26 |
Configuration issue The VPN client provides its own traffic selectors, while the gateway is configured to provide them. |
|
|
27 |
Gateway error The gateway reported an error not supported by the VPN Client. |
|
|
28 |
Login/password error The gateway has rejected the EAP authentication while establishing the VPN connection. |
|
|
30 |
Smart card or token error Cannot access the certificate stored the on the smart card or token. |
|
|
31 |
Captive portal authentication timeout expired No session has been opened on the captive portal. The workstation therefore has no internet connectivity. |
|
|
100 |
Cannot load the VPN configuration No VPN connection has been found in the configuration file. |
|
|
101 |
GINA configuration error A tunnel is active before logon, but has not been configured to be used by the TrustedConnect Panel. |
|
|
102 |
IKE initialization error An error occurred while initializing the IKE daemon. |
|
|
103 |
DNS error A DNS name could not be resolved in the set of rules for the Filtering Mode. |
|
|
200 |
Software activation The software is not activated and the trial period has expired. |
|
Basic cryptography concepts
SHA, RSA, ECDSA and ECSDSA algorithms
Digital signatures generally involve two different types of algorithms:
-
A hash algorithm (SHA: Secure Hash Algorithm)
-
A signature algorithm (RSA: initials of the three inventors, ECDSA: Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm or ECSDSA: Elliptic Curve Schnorr Digital Signature Algorithm)
The strength of RSA encryption depends on the size of the key used. With every doubling of the key length, decryption is six to seven times slower.
According to the NIST and the ANSSI, the recommended minimum key size is 2048 bits.
Hash algorithms can be attacked in either of the following two ways:
-
Hash collision
-
Preimage
A collision occurs when two distinct files produce the same hash value, and it thus becomes possible to substitute one for the other.
Preimage consists in determining the value of a file from its hash value. A second preimage consists in starting out from the hash value to produce a value that is different from the one originally used with the hash function.
According to the ANSSI, the family of SHA-1 hash functions no longer complies with its general security reference system (RGS) and the SHA-2 family should therefore be used. The NIST similarly encourages US federal agencies to switch from SHA-1 to SHA-2.
The rules applied by the SN VPN Client Exclusive follow NIST and ANSSI recommendations. However, if the implemented PKI does not meet these requirements, some of these restrictions can be removed from the software using dynamic parameters.
NOTE
There are several notations in use for the SHA-2 family of algorithms. For example, SHA-2 (256 bits) is also written SHA-256, SHA-2 (384 bits) is also written SHA-384, and so on.
The same applies to elliptic curves. For example, secp256r1 is also referred to as the “P-256 curve”, secp384r1 as the “P-384 curve”, and secp521r1 as the “P-521 curve”.
Accessing certificates
CSP, CNG and PKCS#11: what are the differences?
Certificate management in Windows involves a variety of software and standards regardless of whether certificates are stored in a certificate store, on a token, or on a smart card.
NOTE
Certificates stored on smart cards or tokens are usually copied to the current user's certificate store when the card is inserted into the reader or when the token is connected to the computer.
CSP, CNG, and PKCS#11 are related concepts that all use application programming interfaces (APIs) for certificate management, but the technology implemented is different in each case.
CSP and KSP
In Windows, certificate management traditionally used independent software modules called Cryptographic Service Providers (CSPs). CSPs actually perform algorithms for authentication, encoding, and encryption.
Today, there is a new generation of independent software modules called Key Storage Providers (KSPs). A KSP is used to create, manage, store, and retrieve private keys.
CAPI and CNG
Changing security standards have led Microsoft to deprecate the API associated with CSPs, called Cryptography API (CryptoAPI or CAPI). It has now been replaced with Cryptography API: Next Generation (CNG), which separates cryptographic service providers from key storage providers.
For this reason, version 7.2 and higher of the SN VPN Client Exclusive do not support CSPs and only support the CNG API. You therefore need to ensure that the certificate is imported into the Windows Certificate Store with the correct library (see section Determining a certificate’s container type below).
Machine store and user store
It should also be noted that there are two certificate stores in Windows:
-
The machine store that is available to all users of a machine
-
The user store that is only available to the current user of a machine
NOTE
In command lines, the -user option of the certutil command is used to specify the user store. When it is omitted, the machine store will be used by default.
PKCS#11
In cryptography, PKCS stands for Public Key Cryptography Standards. They are a set of specifications developed by RSA Security.
The PKCS#11 standard provides applications with a method of accessing hardware peripherals (smart cards or tokens), regardless of the type of device. It therefore includes an API serving as a generic interface for a device driver that supports the PKCS#11 standard. This API is supported by version 7.x of the SN VPN Client Exclusive if a corresponding middleware is installed.
Summary
In summary, there are several types of middleware used to access certificates stored on tokens, on smart cards, and in certificate stores (certmgr.msc):
-
CSP stands for Cryptographic Service Provider (deprecated and replaced with CNG): supported up to 7.x versions.
-
CNG stands for Cryptography API: Next Generation: only API supported in 7.x versions. In this case, you must import the certificate into the Windows store using the right library.
-
PKCS#11 stands for Public Key Cryptography Standards: supported by 7.x versions.
Determining a certificate’s container type
CSP and CNG are Microsoft middleware. In Windows, certificates are stored in containers of CNG or CSP type.
To find out the container used for certificates stored in the certificate store, on a token, or on a smart card, you can list the certificates contained in the (user or machine) store. The information returned specifies the type of supplier based on which you can infer the container type (CSP or CNG). The latter will then allow you to determine whether the certificate is compatible with version 7.2 or higher of the SN VPN Client Exclusive
-
To list the certificates contained in the user store, run the following command:
certutil -verifystore -user My
-
To list the certificates contained in the machine store, run the following command:
certutil -verifystore My
Based on the information returned, you can determine the container type as follows. If the supplier is:
-
Microsoft Smart Card Key Storage Provider, the container is of CNG type (compatible with versions 7.2 and higher)
-
Microsoft Base Smart Card Crypto Provider, the container is of CSP type (not compatible with versions 7.2 and higher)
Certificate format
As of version 7 of the SN VPN Client Exclusive, certificates must be in a format that conforms to a specific key size and hash algorithm.
Mandatory
-
Key length: must be at least 2048 bits for RSA certificates
-
Digest algorithm: must be SHA 256, SHA-384, or SHA-512
Optional
CRL checking for user certificates
As of SN VPN Client Exclusive version 7.5, you can check the revocation of the gateway certificate using Online Certificate Status Protocol Stapling (OCSP Stapling). To do this, you must add the dynamic parameter enable_OCSP set to the value true (see section Displaying more parameters).
Gateway certificate
Key Usage extension part
-
Must be present,
-
Must be marked as critical, and
-
Must not contain only the values digitalSignature and/or nonRepudiation
If this is not the case, refer to the dynamic parameter allow_server_extra_keyusage described in section Constraints on the Key Usage extension.
NOTE
In accordance with security requirements, the keyEncipherment value of the Key Usage extension has been deprecated and replaced with the nonRepudiation value, which is now accepted by default. However, SN VPN Client Exclusive version 7.5 continues to accept the keyEncipherment value without needing to use dynamic parameter allow_extra_keyusage.
TIP
We recommend that you give preference to the nonRepudiation value over the keyEncipherment value of the Key Usage extension.
Extended Key Usage extension part
-
Can be present or not,
-
If it is present, it must:
-
Be marked as non-critical, and
-
Only contain either one of the following values
id-kp-serverAuth or
id-kp-serverAuth and id-kp-ipsecIKE
-
If this is not the case, refer to the dynamic parameter allow_server_and_client_auth described in section Constraints on the Extended Key Usage extension
Example of a certificate in Windows
In a Windows PKI, the following is the relationship between a certificate and its extensions:
-
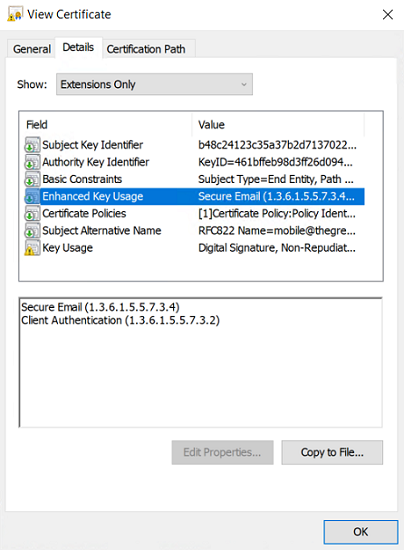
Extended Key Usage:
-
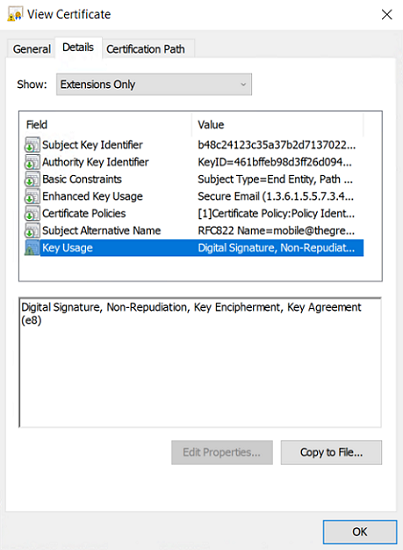
Key Usage:
Example of a certificate log
The extensions are included in a certificate log (file named tgbikeng.log) :
20220826 17:20:23:953 Local0.Info [11204] X509v3 extensions
20220826 17:20:23:956 Local0.Info [11204] Basic constraints :
20220826 17:20:23:960 Local0.Info [11204] CA:FALSE
20220826 17:20:23:965 Local0.Info [11204] Netscape Certificate comment :
20220826 17:20:23:968 Local0.Info [11204] TheGreenBow PKI generated server certificate
20220826 17:20:23:971 Local0.Info [11204] Subject key identifier :
20220826 17:20:23:974 Local0.Info [11204] FB:D6:5A:EF:FE:1B:DC:68:90:66:B9:D7:47:45:EA:B5:86:97:4A:B3
20220826 17:20:23:978 Local0.Info [11204] Authority key identifier :
20220826 17:20:23:981 Local0.Info [11204] keyIdentifier: 6F:6D:B8:A5:0B:EA:64:82:2E:B4:5F:0A:35:53:8B:80:05:4C:7B:0E
20220826 17:20:23:984 Local0.Info [11204] authorityCertIssuer: C = FR, ST = Ile-de-France, L = Paris, O = TheGreenBow, OU = QA40, CN = Root CA
20220826 17:20:23:988 Local0.Info [11204] authorityCertSerialNumber: 10:00
20220826 17:20:23:990 Local0.Info [11204] Key usage : critical
20220826 17:20:23:995 Local0.Info [11204] Digital signature
20220826 17:20:24:000 Local0.Info [11204] Extended key usage :
20220826 17:20:24:003 Local0.Info [11204] Server authentication
User certificate
Warning messages may be displayed in the Console for a user certificate, but you do not need to remove any restrictions from the VPN Client.
Certificate authentication methods
SN VPN Client Exclusive supports the following certificate authentication methods:
-
Method 1: RSA Digital Signature with SHA-2 [RFC 7296]
-
Method 9: ECDSA “secp256r1” with SHA-2 (256 bits) on the P-256 curve [RFC 4754]
-
Method 10: ECDSA “secp384r1” with SHA-2 (384 bits) on the P-384 curve [RFC 4754]
-
Method 11: ECDSA “secp521r1” with SHA-2 (512 bits) on the P-521 curve [RFC 4754]
-
Method 14: Digital Signature RSASSA-PSS, RSASSA PKCS1 v1_5, and Brainpool with SHA-2 (256/384/512 bits) [RFC 7427]
-
Method 214: ECDSA “BrainpoolP256r1” with SHA-2 (256 bits) on the BrainpoolP256r1 curve (only available with gateways that support this method)
The default authentication method used for RSA certificates (RSASSA-PSS or RSASSA-PKCS1-v1_5) is method 14 with an RSASSA-PSS signature. If the gateway/firewall uses method 14 with an RSASSA-PKCS1-v1.5 signature, the VPN Client will reject the certificate and the following message will be displayed in the Console:
RSASSA-PKCS1-v1_5 signature scheme not supported with authentication method 14
In the event that the gateway does not support method 14 with an RSASSA PSS signature, you can configure the VPN Client to use method 14 with an RSASSA-PKCS1-v1_5 signature, by adding the dynamic parameter Method14_RSASSA_PKCS1 with a value set to true or yes (see section Displaying more parameters).
In the event that the gateway does not support method 14 with an RSASSA-PKCS1-v1_5 signature, you can configure the VPN Client to use method 1 with an RSA and SHA-2 digital signature, by adding the dynamic parameter Method1_PKCS1v15_Scheme with a value set to 04 (SHA-256), 05 (SHA-384) or 06 (SHA-512) (see section Displaying more parameters). The VPN Client will reject any other value entered.
The authentication method used for ECDSA certificates (elliptical curves) depends on the elliptical curve used in the certificate: ECDSA with SHA-256 on the P-256 curve, ECDSA with SHA-384 on the P-384 curve, ECDSA with SHA-512 on the P-521 curve or ECDSA with SHA-256 on the BrainpoolP256r1 curve.
When the VPN Client needs to create a signature for a Brainpool user certificate, authentication method 14 is used by default, which is appropriate for a gateway that is not running in Restricted mode. If this type of certificate is to be used with a gateway running in Restricted mode, the dynamic parameter use_method_214 must be added and set to the value true (see section Displaying more parameters). The NID_sha256, NID_sha384, or NID_sha512 message digest algorithm is used for signature depending on the key size.
-
The SHA-1 algorithm cannot be used in digital signatures.
-
SN VPN Client Exclusive will reject RSA certificates with a key size lower than 2048 bits.
-
SN VPN Client Exclusive will reject ECDSA certificates with a key size lower than 256 bits.
SN VPN Client Exclusive technical data
General
|
Windows version |
Windows 11 64-bit |
|
Languages |
Arabic, Chinese (simplified), Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, Farsi, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hindi, Hungarian, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Norwegian, Polish, Portuguese, Russian, Serbian, Slovenian, Spanish, Thai, Turkish |
Operating mode
|
Invisible mode |
Automatically open tunnel when traffic is detected Control access to VPN configurations Hide part or all the interfaces |
|
Gina |
Open a tunnel before Windows logon using: GINA/Credential providers on Windows 10 |
|
Scripts |
Run configurable scripts when opening or closing a VPN tunnel |
|
Remote Desktop Sharing |
Open a remote computer with a single click via RDP and VPN tunnel |
|
TrustedConnect Panel |
Automatically open tunnel with Always-On and trusted network detection (TND) |
Connection/Tunnel
|
Connection mode |
Peer-to-gateway |
|
Networks |
IPv4 and IPv6 |
|
Protocols |
IPsec/IKEv2 SSL/OpenVPN |
|
CP mode |
Automatically retrieve network parameters from the VPN gateway |
Cryptography and authentication
|
Encryption, Key groups and Hashing (IKEv2) |
Symmetric: AES CBC/CTR/GCM 128/192/256 bits Diffie-Hellman: DH 14 (MODP 2048), DH 15 (MODP 3072), DH 16 (MODP 4096), DH 17 (MODP 6144), DH 18 (MODP 8192), DH 19 (ECP 256), DH 20 (ECP 384), DH 21 (ECP 521), DH 28 (BrainpoolP256r1) Hashing: SHA-2 (256/384/512 bits) |
|
TLS security suites (OpenVPN) |
TLS 1.2—Medium TLS 1.2—High TLS 1.3:
|
|
Encryption and Hashing (OpenVPN) |
Symmetric: AES-128-CBC, AES-192-CBC and AES-256-CBC Hashing: SHA-2 (224/256/384/512 bits) |
|
Authentication |
|
|
Certificate authentication methods |
|
|
PKI |
|
Miscellaneous
|
NAT/NAT-Traversal |
NAT-Traversal Draft 1 (enhanced), Draft 2, Draft 3 and RFC 3947, IP address emulation, includes support for: NAT_OA, NAT keepalive, NAT-T aggressive mode, NAT-T in forced, automatic or disabled mode |
|
DPD |
RFC 3706. Detection of inactive IKE endpoints. |
|
Redundant gateway |
Redundant gateway management, automatically selected when DPD is triggered (inactive gateway) |
Administration
|
Deployment |
Silent installation using Microsoft Installer (MSI) |
|
VPN configuration management |
Import and export options for VPN configurations Secure import/export using passwords, encryption, and integrity control |
|
Automation |
Ability to open, close, and monitor a tunnel using command lines (batch and scripts) Ability to start and quit the software using batches |
|
Logs and traces |
IKE/IPsec and SSL/OpenVPN log Console and trace mode can be enabled Administrator logs: local file, Windows Event Log, syslog server |
|
Upgrades |
Check for available updates from within the software |
|
License and activation |
Licenses available on a subscription basis, manual/automatic/silent activation |