Understanding the impact of changing the EWC URL database
This section explains the impact of changing the EWC URL database, and how to view changes that are automatically made after the database is installed. We strongly advise you to read this section.
Impact on the classification logic and construction of the URL/SSL policy
The classification logic has changed after the installation of the new database: the URL/SSL filter policy must now be in blacklist mode. This requires the following considerations to be taken into account:
-
The URL categories to be prohibited must be placed above rules that allow other categories,
-
You are strongly advised to build the URL/SSL filter policy in several sections and by following a particular order. We recommend these sections:
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 - Compromised URLs |
Category that groups malicious URLs, and which Stormshield's security teams continuously update |
|
2 - Always block |
Illegal, dangerous and violent content |
|
3 - Always pass, never decrypt (GDPR) |
Content that requires the protection of user data (banking, healthcare, etc.) |
|
4 - Always pass, can be decrypted |
Content relating to the organization's business sector and which users require for work |
|
5 - Block recommended |
Content that should be blocked, but without preventing users from visiting websites that fall under "Always pass" sections |
|
6 - Pass recommended |
Content that should be allowed, so that users are not prevented from browsing the Internet (in particular, the URL categories unknown, misc, hosting and computersandsoftware). |
|
7 - Pass (Any) |
Equivalent to a pass all rule. Action applied to any website that has not been categorized in previous sections |
- In section 6 - Pass recommended, you are strongly advised to allow the URL categories unknown, misc, hosting and computersandsoftware. If these categories are blocked, the display of websites that use external resources (images, .css, .js, write policies, etc.) may be affected, even if the visited website is in an allowed category.
Impact on URL/SSL filter rules
The way URL/SSL filter rules are processed when the database is changed depends on whether the former and new URL categories match. There are several possible matches:
-
Categories exactly match;
-
Categories partially match;
-
Categories do not match, the former category has no equivalent;
-
Categories do not match, the new category has no equivalent.
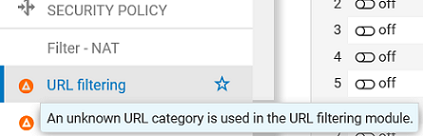
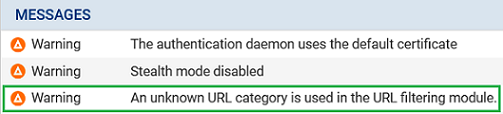
After the database is changed, administrator intervention is required in some scenarios to fix inconsistencies or errors in the configuration. Warning messages appear in the firewall's administration interface to identify such inconsistencies:
-
In the menu on the left, in front of the URL filtering and SSL filtering modules,
-
In the Dashboard, in the Messages section.
Categories exactly match
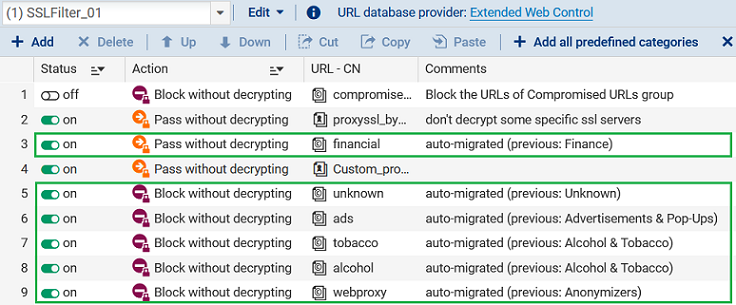
The Former EWC URL categories that are exact matches of new categories are automatically replaced in the URL/SSL filter rules in question.
The rule is processed as follows during migration:
- The former category is replaced with the new equivalent category,
- The rule keeps the status (enabled/disabled) and action that it had before it was migrated,
- An "auto-migrated (previous: name_former_category)" comment will be associated with it.
Categories partially match
The Former EWC URL categories that partially match new categories may have been grouped under a single new category.
EXAMPLES
The categories Child abuse and Criminal activity fall under the new category illegal.
The categories Religion and Cults fall under the new category religion.
Separate former categories may have been used in different rules. There are two situations in which rules would apply the same or different actions (pass, block, decrypt, etc.). In each case, rules are processed differently when they are migrated.
Category appearing in rules that apply the same action
In the first filter rule encountered that uses the former category:
- The former category is replaced with the new equivalent category,
- An "auto-migrated (previous: name_former_category)" comment will be associated with it.
The following rules that used the former category will be deleted from the URL/SSL filter profile to avoid creating duplicate rules.
EXAMPLE
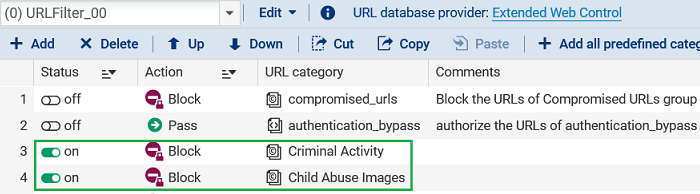
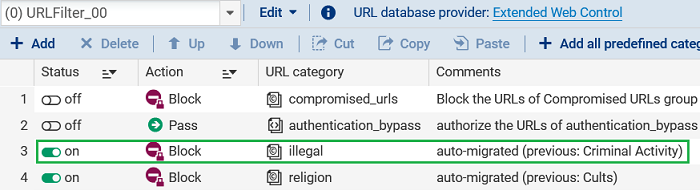
The first rule that blocks the former category Child abuse, which now falls under the new category illegal, will be retained. The second rule that blocks the former category Criminal activity, which now falls under the new category illegal, will be deleted since the first rule already blocks the category.
Before migration:
After migration:
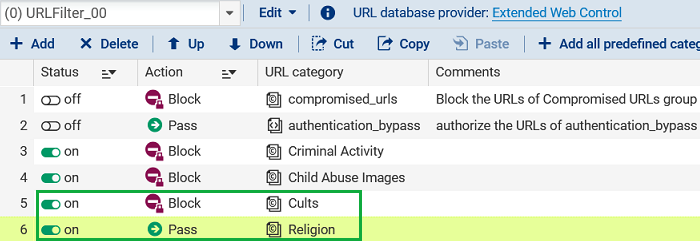
Category appearing in rules that apply different actions
For each rule:
-
The former category is replaced with the new equivalent category,
-
An "auto-migrated (previous: name_former_category)" comment will be associated with each rule.
These rules will generate a warning in the consistency checker: administrator intervention is required to fix this situation and validate the policy.
Before migration:
After migration:

Categories do not match, the former category has no equivalent
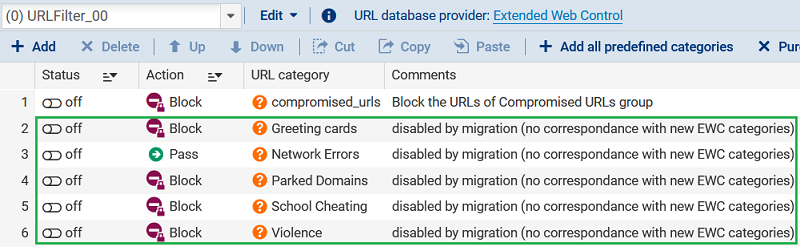
A rule that uses Former EWC URL categories without any equivalence with new categories is processed as follows:
- The rule is retained with the former URL category, but is disabled,
- A "disabled by migration (no correspondence with new EWC categories)" comment will be associated with it.
Categories do not match, the new category has no equivalent
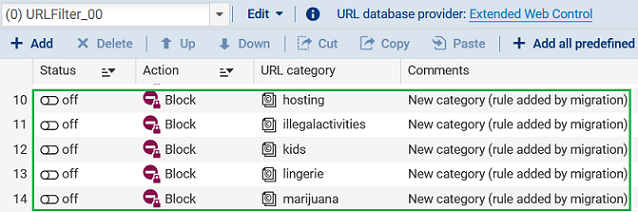
The new provider's URL database introduces New EWC URL categories without any equivalence with former categories. For each of these categories:
- A disabled rule with a block action is added right at the end of the URL/SSL filter profile,
- A "New category (rule added by migration)" comment is associated with it.
Impact on URL category groups
The way URL category groups are processed when the database is changed depends on whether the former and new URL categories match. There are two possible situations.
Exact or partial category match
The Former EWC URL categories that are exact matches of new categories and Former EWC URL categories that partially match new categories, are automatically replaced with the new equivalent category(ies) in the URL category groups that may have been created before the migration.
EXAMPLES
The category Finance has been replaced with the new category financial. The categories Child abuse and Criminal activity have been replaced with the new category illegal.
Categories do not match, the former category has no equivalent
The Former EWC URL categories without any equivalence with new categories are deleted from URL category groups that may have been created before the migration.
In this case, no warnings will be displayed in the firewall's administration interface: administrator intervention is required to check this situation and fix the groups.
Impact on authentication exception rules in the filter policy
Former categories will not be replaced in authentication exception rules in the filter policy.
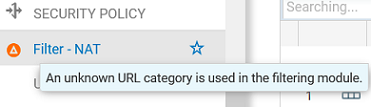
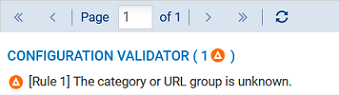
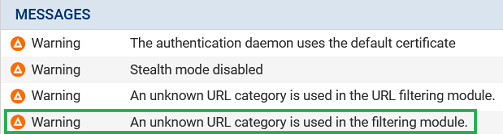
After the database is changed, administrator intervention is required to fix errors and validate the policy. Warning messages appear in the firewall's administration interface to identify such inconsistencies:
-
In the menu on the left, in front of the name of the Filter - NAT module,
-
In the Filter - NAT module, in the filter policy rules,
-
In the Filter - NAT module, in the filter consistency checker,
-
In the Dashboard, in the Messages section.

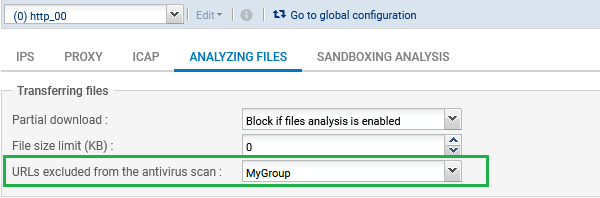
Impact on URLs excluded from the HTTP protocol antivirus scan
Check that the content of groups/URLs specified in the URLs excluded from the HTTP protocol antivirus scan (Protocols > HTTP > File scan tab) still complies with the desired policy.
No warnings will be displayed in the firewall's administration interface: administrator intervention is required to check this situation and fix it.