Configuring the SSL VPN service
This section explains how to enable and configure the SSL VPN service.
Go to Configuration > VPN > SSL VPN.
NOTE
As of SNS version 4.8.5, if the LZ4 compression feature in the SSL VPN service is enabled, a warning message will automatically appear when the module opens, encouraging you to disable the feature. This scenario is described in the section Troubleshooting.
Enabling the SSL VPN service
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
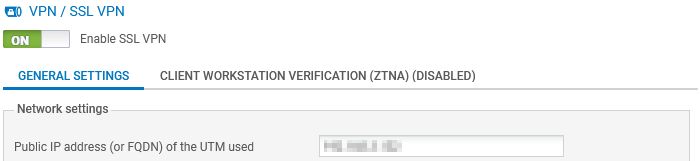
Enable SSL VPN
|
Set the selector to ON to enable the SSL VPN service. |
Configuring the general settings of the SSL VPN service
On SNS in versions 4.8 and higher, these settings can be configured in the General settings tab. On SNS 4.3 LTSB versions, there is no tab.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Enable client workstation verification (ZTNA)
|
On SNS in version 5, set the selector to ON to enable the verification of client workstation compliance. When it is enabled:
On SNS 4.8 versions, the verification can be enabled in the Client workstation verification (ZTNA) tab (see Configuring client workstation verification (ZTNA)). On SNS 4.3 LTSB versions, this feature is not available. |
Network settings section
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Public IP address (or FQDN) of the UTM used |
Indicate the IP address that users must use to reach the SNS firewall in order to set up VPN tunnels. You can indicate either an IP address or FQDN.
|
| Available networks or hosts |
Select the object representing the networks or hosts that will be reached through the VPN tunnel. This object makes it possible to automatically set on the workstation the routes needed to reach resources that can be accessed via the VPN.
You will need to set filter rules to more granularly allow or prohibit traffic between remote workstations and internal resources. You may also need to set static routes for access to the network assigned to VPN clients on corporate network devices located between the SNS firewall and the internal resources provided. |
|
Network assigned to clients (UDP)
Network assigned to clients (TCP) |
Select the object corresponding to the network that has been assigned to VPN clients in UDP and TCP. The network mask must not be smaller than /28. If you assign two networks, VPN client will always choose the UDP network first to ensure better performance. Choosing the network or sub-networks:
|
| Maximum number of simultaneous tunnels allowed |
The number appears automatically. This number corresponds to the lowest value, either the number of tunnels allowed on the SNS firewall (see Requirements), or the number of sub-networks available for VPN clients. For sub-networks:
|
DNS settings sent to client section
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Domain name | Enter the domain name assigned to the SSL VPN clients so that they can resolve their host names. |
|
Primary DNS server
Secondary DNS server |
Select the object representing the DNS server to be assigned. |
Advanced properties section
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable DCO kernel acceleration |
On SNS in version 5, select the checkbox to enable the DCO (Data Channel Offload) kernel acceleration feature. This option is enabled by default in factory configuration. On SNS in version 4, this feature is not available.
This feature transfers the encryption/decryption of data packets passing through SSL VPN tunnels to the operating system kernel. This increases the performance of UDP-based tunnels and enables the SSL VPN service to process the setup of many more UDP tunnels. However, this feature is not compatible with TCP-based tunnels, and downgrades their performance. Ensure that you disable it if you are using such tunnels. NOTE
|
| Public IP address of the UTM for the SSL VPN (UDP) |
In either of the following cases, you need to select the object representing the IP address used for setting up UDP SSL VPN tunnels:
|
| Port (UDP)
Port (TCP) |
The listening ports of the SSL VPN service can be changed. Note:
|
| Interval before key renegotiation (seconds) |
You can change the length of time (14400 seconds by default, or 4 hours) after which the keys used by the encryption algorithms will be renegotiated. During this operation:
|
| Use DNS servers provided by the firewall |
You can instruct VPN clients to include the DNS servers retrieved via the SSL VPN in the workstation's (Windows only) network configuration. If DNS servers are already defined on the workstation, they may be queried. |
| Prohibit use of third-party DNS servers |
You can instruct VPN clients to exclude the DNS servers that have already been defined in the workstation's (Windows only) configuration. Only DNS servers sent by the SNS firewall can be queried. |
Scripts to run on the client
In Windows, the Stormshield SSL VPN client can run .bat scripts when an SSL VPN tunnel is opened or closed. In these scripts, you can use:
-
Windows environment variables (%USERDOMAIN%, %SystemRoot%, etc.),
-
Variables relating to the Stormshield SSL VPN client: %NS_USERNAME% (user name used for authentication) and %NS_ADDRESS% (IP address assigned to the SSL VPN client).
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Script to run when connecting |
Select the script to run when the VPN tunnel is opened. Example of a script that makes it possible to connect the Z: network drive to the shared network: NET USE Z: \\myserver\myshare |
| Script to run when disconnecting |
Select the script to run when the VPN tunnel is closed. Example of a script that makes it possible to disconnect the Z: network drive from a shared network: NET USE Z: /delete |
Certificates
Select the certificates that the SNS firewall’s SSL VPN service and the Stormshield SSL VPN client must present to set up a tunnel. They must be issued from the same certification authority.
The default suggestions are the certification authority dedicated to the SSL VPN, and a server certificate and a client certificate created when the firewall was initialized.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Server certificate |
Select the desired certificate. The |
| Client certificate | Select the desired certificate. Client certificates with a TPM-protected private key cannot be selected as the private keys of such certificates must be available in plaintext (unencrypted) in the VPN configuration that is distributed to VPN clients. |
Configuration
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Export the configuration file |
Click on this button to export the SSL VPN configuration in .ovpn format. |