Configuring the VPN client
On the user's Microsoft Windows workstation:, open the connection window of the VPN client:
- Right-click on the icon found in the Windows system tray (hidden icons):

- Select Connection panel.
For the purposes of the example presented in this tutorial, we assumed that mobile clients could access two separate, discontiguous networks via IPsec: Network 192.168.1.0/24 and Network 192.168.128.0/24.
Two separate Phase 2 configurations therefore need to be created for this configuration – one for each network. You need to create as many Phase 2 configurations as the number of discontiguous networks that the VPN clients can reach.
Do note that each of these Phase 2 configurations will use a separate VPN client IP address.
Configuring Phase 1
- In the VPN configuration tree, right-click on IKEv2.
- Select New IKE auth.
An entry named Ikev2Gateway by default is added to the IKEv2 tree. - Right-click on Ikev2Gateway and select Rename to give this entry the name of your choice (Ikev2GwStandard in the example).
- Click on this entry.
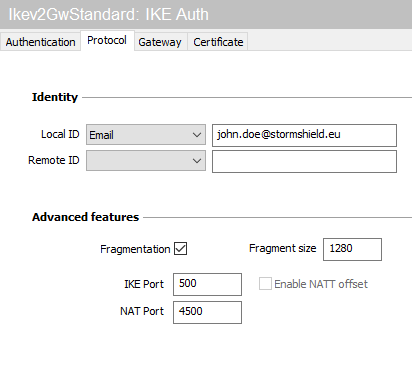
- In the Protocol tab > Identity > Local ID field, select E-mail from the drop-down list and enter the e-mail address of the workstation user.
- In the Protocol tab > Advanced features section, select the Fragmentation checkbox and indicate the size of IKE fragments as defined on the firewall (1280 bytes according to Stormshield’s recommendations).
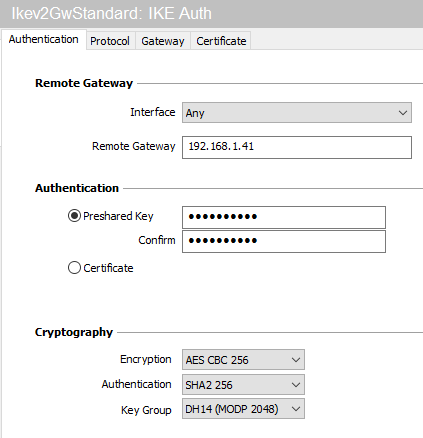
- In the Authentication tab > Remote router address > Remote router address field, enter the public IP address or FQDN of the firewall with which the VPN client must set up a tunnel.
If you choose to use an FQDN, ensure that the DNS servers on the workstation have resolved it before you set up the tunnel. - In the Authentication tab > Authentication > Preshared key field, enter and confirm the pre-shared key defined for this user on the firewall.
- Click on the upper menu Configuration > Save to save this configuration.
Configuring Phase 2 for the first network
- In the VPN configuration > IKEv2 tree, right-click on the Phase 1 configuration created earlier (Ikev2GwStandard in the example).
- Select New Child SA.
An entry named Ikev2Tunnel by default is added to the selected Phase 1 configuration. - Right-click on Ikev2Tunnel and select Rename to give this entry the name of your choice (Ikev2Net1Tunnel in the example).
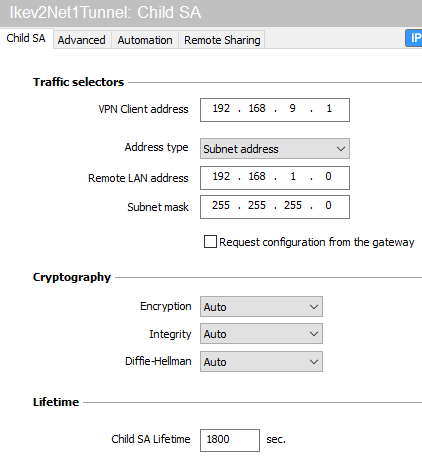
- In the Child SA tab > Traffic selectors > VPN Client address field, enter the IP address of the client (192.168.9.1 in the example). This address must belong to the network defined in the section Defining a network object that contains IP addresses assigned to mobile peers.
- In the Child SA tab > Traffic selectors > Address type field, select Network address.
- In the Remote network address field, enter the address of the first reachable network (192.168.1.0 in the example).
- In the Subnet mask field, enter the mask associated with this network (255.255.255.0 in the example).
- In the Advanced tab > Alternative servers, if necessary, define a DNS suffix and Alternative (DNS) Servers to be used for this IPsec VPN tunnel.
- Click on the upper menu Configuration > Save to save this configuration.
The IKEv2 tunnel to reach the first network in the example is now configured.
Configuring Phase 2 for the second accessible network
Apply the method described in the section Configuring Phase 2 for the first network to define the tunnel that enables access to the second network.
In the example given, the parameters used for the second tunnel are:
- Phase 2 name: Ikev2Net2Tunnel
- VPN client IP address: 192.168.9.2
- Network IP address: 192.168.128.0
- Mask: 255.255.255.0