Zero Trust Data Format
Zero Trust Data Format (ZTDF) is an interoperable data security wrapper. It seamlessly understands all variations of the TDF metadata standard, allowing organizations to build custom policy enforcement points. ZTDF facilitates secure collaboration and data sharing, enabling files, messages, and documents to be shared across borders and classifications.
It allows organizations to integrate data-centric governance controls into legacy and next-generation applications, ensuring sensitive information remains protected. ZTDF format provides auto-enforcing granular access controls and grants access only to authorized individuals.
ZTDF with symmetric KAS
Stormshield has developed a variant of ZTDF to simplify its use and enable it to work with your KMaaS. The DEK used to encrypt your data is symmetrically encrypted by a Key Encryption Key (KEK) via the KMaaS KAS feature.
Simplified version of the encryption workflow:
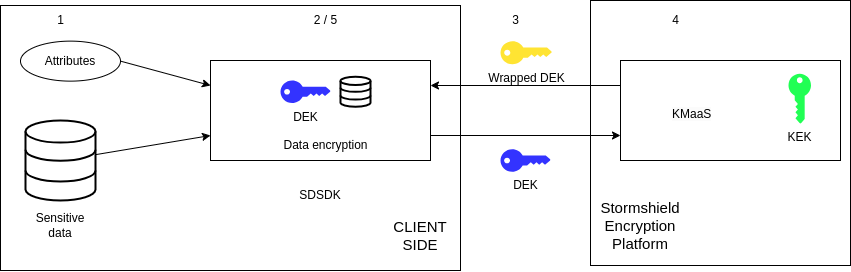
- The user provides the SDK with the data to be encrypted. They can also provide a list of attributes which will subsequently be used for ABAC.
- The SDK generates a DEK to encrypt the data. It also generates a manifest that includes all the data that will be useful for decryption, the attributes, and information to ensure the integrity of the data or attributes.
- The DEK is sent to the KMaaS.
- The DEK is wrapped with a KEK.
- The wrapped DEK is returned and stored in the manifest, the ZTDF carries its own security.
Simplified version of the decryption workflow:
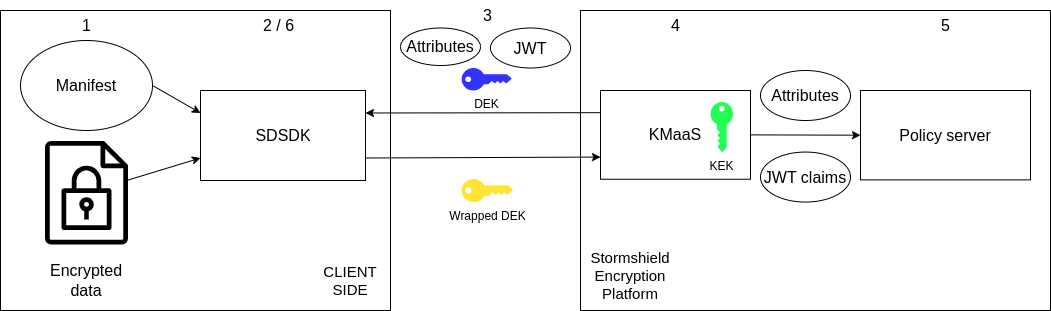
- The user provides the SDK with the encrypted data and the manifest.
- The SDK extracts the attributes and wrapped DEK from the manifest.
- The wrapped DEK and attributes with authentication credentials are sent to the SDK.
- Data attributes are sent to the policy (see 5) and the wrapped DEK is decrypted and returned to the SDK.
- Data attributes and other information (e.g., custom JWT token claims) are evaluated by the policy server. Policy server rules are at the administrator's discretion. For more information on writing Policy rules refer to the KMaaS documentation.
- Data integrity is verified, then the data is decrypted on the client side.
ZTDF with asymmetric KAS (Offline encryption)
To support offline or disconnected scenarios, the SDK also provides an asymmetric encryption mechanism. In this mode, the encryption process does not require any communication with the KMaaS. The Data Encryption Key (DEK) is wrapped locally using a public Key Encryption Key (KEK) that you provide.
Decryption, however, remains an online process. The KAS uses its corresponding private key to unwrap the DEK after a successful policy evaluation.
Simplified version of the asymmetric encryption workflow:
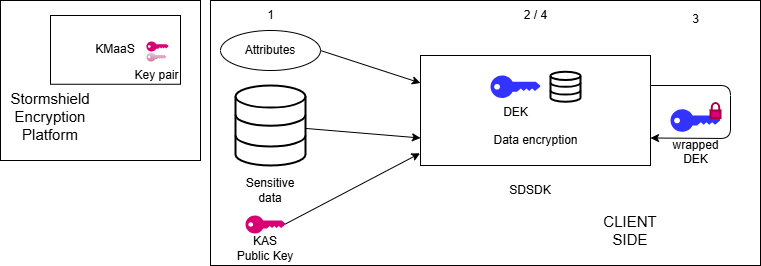
- The user provides the SDK with the data to be encrypted, an optional list of attributes, and a public KEK (with its identifier
kid). - The SDK generates a DEK to encrypt the data.
- The SDK locally wraps the DEK using the provided public KEK. No call is made to the KMaaS.
- The SDK generates a manifest containing the wrapped DEK, attributes, and integrity information. The resulting ZTDF object is self-contained and ready for storage or transmission.
Asymmetric decryption workflow:
The decryption workflow is functionally identical to the symmetric version from the user's perspective.
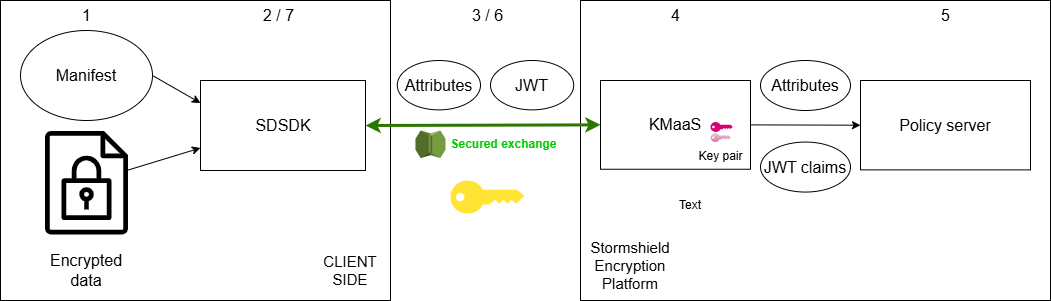
- The user provides the SDK with the encrypted data and the manifest.
- The SDK extracts the wrapped DEK and attributes.
- These are sent to the KMaaS for unwrapping and policy evaluation against the OPA server.
- The KMaaS uses its private key to unwrap the DEK.
- Data attributes and other information (e.g., custom JWT token claims) are evaluated by the policy server. Policy server rules are at the administrator's discretion. For more information on writing Policy rules refer to the KMaaS documentation.
- The DEK is returned to the SDK.
- The SDK verifies data integrity and decrypts the data on the client side.
NOTE
Security of the Data Encryption Key (DEK) in Transit.
During the asymmetric decryption process, the communication between the SDK and the KAS is secured. To protect the DEK on its return path to the client, the SDK generates a temporary (ephemeral) asymmetric key pair. It sends the public key to the KMaaS, which then encrypts the DEK with this public key before sending it back.
This mechanism ensures that the DEK remains confidential end-to-end, providing an additional layer of security on top of the standard TLS channel protection. This entire process is managed automatically by the SDK and is transparent to the developer.