Connectivity with Amazon VPC
The aim here is to connect a local network to an Amazon VPC (virtual private cloud). To do so, Amazon offers the possibility of creating two routed tunnels between the local firewall and the Amazon cloud, and then routing this traffic over BGP.
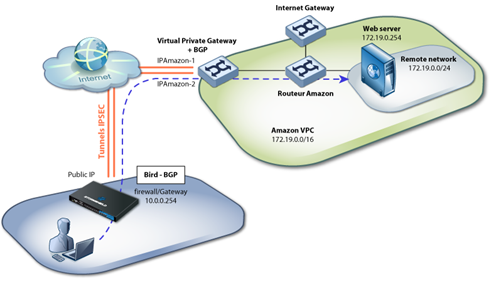
Amazon VPC configuration
Follow the steps below:
- Create an Amazon VPC.
- Create a subnet in this VPC.
- Configure routing in this VPC.
- Create a dynamic VPN connection to this firewall through the Amazon Virtual Private Gateway object.
- Create ACLs to allow local traffic to the web server.
- Routing: allow routes to be announced to the VPC routing table.
Excerpt of the configuration help provided by Amazon during the configuration of the service:
The Customer Gateway inside IP address should be configured on your tunnel interface.
Outside IP Addresses:
- Customer Gateway: Firewall/Gateway public IP,
- Virtual Private Gateway: IPAmazon-1.
Inside IP Addresses:
- Customer Gateway : 169.254.254.66/30,
- Virtual Private Gateway : 169.254.254.65/30.
Configure your tunnel to fragment at the optimal size:
- Tunnel interface MTU: 1436 bytes.
#4: Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Configuration:
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGPv4) is used within the tunnel, between the inside IP addresses, to exchange routes from the VPC to your home network. Each BGP router has an Autonomous System Number (ASN). Your ASN was provided to AWS when the Customer Gateway was created.
BGP Configuration Options:
- Customer Gateway ASN: 65000,
- Virtual Private Gateway ASN: 9059,
- Neighbor IP Address: 169.254.254.65,
- Neighbor Hold Time: 30.
Configure BGP to announce routes to the Virtual Private Gateway. The gateway will announce prefixes to your customer gateway based upon the prefix you assigned to the VPC at creation time.
Tunnel configuration
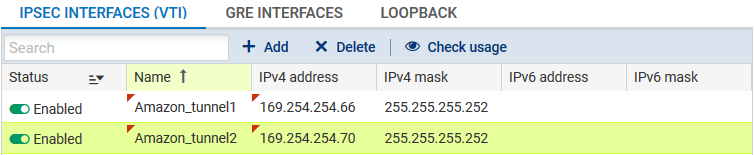
In Configuration > Network > Virtual interfaces, the IPsec interfaces tab allows you to define the interfaces in question:
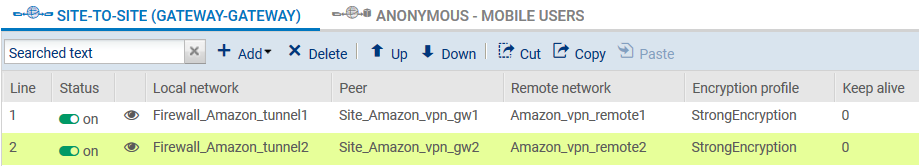
In Configuration > VPN > IPsec VPN, Site-to-site (gateway-gateway) tab, you can define the tunnels below by using the following objects:
- Site_Amazon_vpn_gw1: IPAmazon-1,
- Site_Amazon_vpn_gw2: IPAmazon-2,
- Amazon_vpn_remote1: 169.254.254.65,
- Amazon_vpn_remote2: 169.254.254.69.
BGP configuration
Here, we are choosing to export only the network 10.0.1.0/24
filter filter_net_in {
if net = 10.0.1.0/24 then {
accept;
}
else reject;
}
protocol bgp router1 {
local as 65000;
neighbor 169.254.254.65 as 9059;
source address 169.254.254.66;
hold time 30;
multihop;
ipv4 {
import all;
export filter filter_net_in;
};
}
protocol bgp router2 {
local as 65000;
neighbor 169.254.254.69 as 9059;
source address 169.254.254.70;
hold time 30;
multihop;
ipv4 {
export filter filter_net_in;
import all;
};
}