Encrypting and decrypting sensitive data
The table below describes the steps of the encrypt and decrypt procedure.
Click on a link to open the corresponding procedure in this guide.
| Steps | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
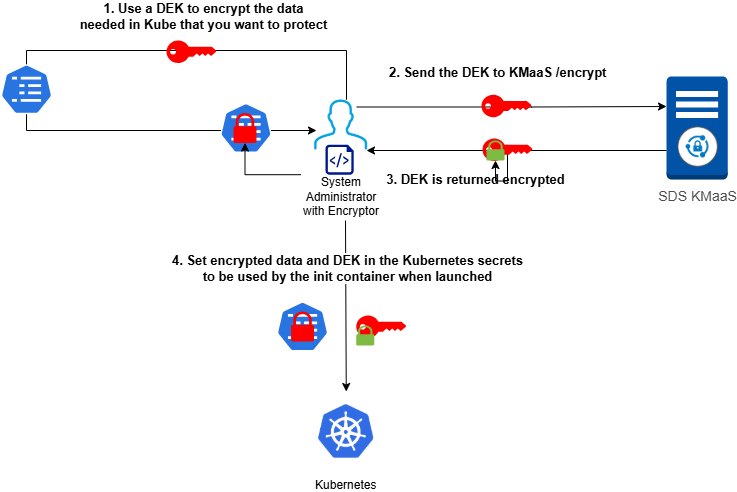
Encrypt the sensitive data using the encryptor.cjs script. The result is the Encrypted sensitive data, a base64-encoded string containing the encrypted data, the encrypted DEK, and some metadata. |
| 2 |
Create the Kubernetes secrets for securely storing the KMaaS API key and the Encrypted sensitive data. |
| 3 | Configure the pod.yaml Kubernetes manifest by setting the KMaaS parameters. |
| 4 | Decrypt the sensitive data in SDS for Kubernetes init container by deploying the sdskub pod. |
Encrypt workflow
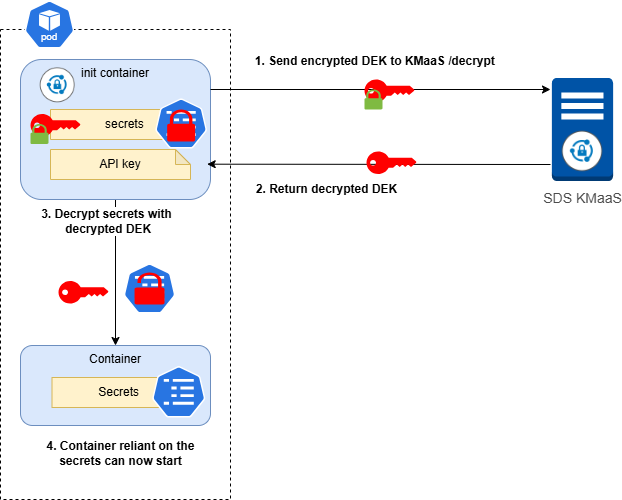
Decrypt workflow
The encryptor.cjs script encrypts your sensitive data before you set it as a Kubernetes secret. We recommend that you perform this operation in a secure and trusted environment, as you will handle data in clear text. In addition, be sure to clean up your command history.
-
Run the encryptor.cjs script provided in the sds-kubernetes-init-container-<version>.tar archive.
$ node encryptor.cjs "sensitive data"
The data to be encrypted must not exceed 10 KB.
The command result is similar to:
$ [INFO] {"encrypted_sensitive_data":
'BKJhY6RhYVBHD4jEAjHoP6FCVF7Ejnifk7prOWqJu88dibUOGuU+8Rai6DEl67Wdczs9KncrRQAYj2qqwjFNvdicASV4='} -
Copy the value of the encrypted sensitive data to use it in next procedure.
In Kubernetes, you must create two secrets for the sensitive data that you have encrypted:
-
A secret containing the KMaaS API key that will be used to authenticate to the KMaaS during decryption,
-
A secret containing the encrypted sensitive data.
-
Create a secret from the base64 API key string set in section Configuring the KMaaS. It allows Kubernetes to connect to the KMaaS to decrypt the sensitive data.
For example, you can use the following command:$ kubectl create secret generic sdskub-kmaas --from-literal=api-key="NCH2aG9yaXplZEFwaUtleTpvY2dZWENFSzY2UHJUSTYxTnkzSmtBRkxyM0JaL0x4Vw=="
-
Create a secret from the encrypted sensitive data obtained in section Encrypting sensitive data.
For example, you can use the following command:$ kubectl create secret generic sdskub-encrypted-data --from-literal=encrypted-sensitive-data="BKJhY6RhYVBHD4jEAjHoP6FCVF7Ejnifk7prOWqJu88dibUOGuU+8Rai6DEl67Wdczs9KncrRQAYj2qqwjFNvdicASV4="
In the above examples, two secrets are created:
-
sdskub-kmaas is the secret containing the KMaaS API key,
-
sdskub-encrypted-data is the secret containing the encrypted sensitive data.
You must configure the pod manifest to indicate that such application will be able to use such and such secrets via the init-container.
-
From the sds-kubernetes-init-container-<version>.tar archive file, retrieve the sample pod.yaml manifest file.
-
In the file, replace the name and key placeholders values of the following parameters:
Parameter Description KMAAS_API_KEY Name and key of the secret containing the KMaaS API key (sdskub-kmaas and api-key in our example).
ENCRYPTED_SENSITIVE_DATA Name and key of the secret containing the encrypted sensitive data obtained with the encryptor.cjs script (sdskub-encrypted-data and encrypted-sensitive-data in our example). OUTPUT_SENSITIVE_DATA_PATH Path used by the init container to write the decrypted sensitive data. It must be the path of a volume shared between the init container and the main container (/mnt/shared/sensitive-data in our example).
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: sdskub
spec:
restartPolicy: Never
initContainers:
- name: sdskub-init-container
image: IMAGE_TAG:VERSION
env:
- name: NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTS
value: /etc/ssl/certs/kmaas_ca.crt
- name: KMAAS_API_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: sdskub-kmaas
key: api-key
- name: ENCRYPTED_SENSITIVE_DATA
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: sdskub-encrypted-data
key: encrypted-sensitive-data
- name: OUTPUT_SENSITIVE_DATA_PATH
value: /mnt/shared/sensitive-data
volumeMounts:
- name: sdskub-shared
mountPath: /mnt/shared
- name: trusted-ca-store-volume
mountPath: /etc/ssl/certs/kmaas_ca.crt
subPath: kmaas_ca.crt
readOnly: false
containers: # It is an example container, you have to replace it by your own image
- name: sdskub-main-container
image: busybox:1.28
command: ["cat", "/mnt/shared/sensitive-data"]
volumeMounts:
- name: sdskub-shared
mountPath: /mnt/shared
volumes:
- name: sdskub-shared
emptyDir: { medium: Memory }
- name: trusted-ca-store-volume
secret: {secretName: trusted-ca-store}
The environment variable NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTS used in this example contains the path to the KMAAS CA file that is mounted as a volume. This allows a TLS connection to be opened between the sdskub-init-container and the KMAAS.
In our example, the command to create the secret would be:
kubectl create secret generic trusted-ca-store --from-file=<PATH_TO_KMAAS_CA>
This is only useful if your KMaas CA certificate is not trusted by default.
To decrypt the sensitive data, you must deploy the sdskub pod.
-
Run the following command to apply the manifest and deploy the pod:
$ kubectl apply -f pod.yaml
The sensitive data is decrypted and stored in the shared volume specified by the OUTPUT_SENSITIVE_DATA_PATH parameter. If the decryption is successful, the logs are similar to:
$ kubectl logs sdskub -c sdskub-init-container
$ { "timestamp": "2025-05-21T08:54:17.262Z", "severity": "info", "application_version": "1.0.0", "kind": "domain", "category": "secrets", "action": "decrypt", "secret_path": "/mnt/shared/sensitive-data", "url": "https://kmaas-host:3000/api/v1/025f02fe-bee2-231c-bf76-b5ead30327c0/kas/decrypt"}
In the above example, the decrypted sensitive data is stored in /mnt/shared/sensitive-data.
For more information about logs, refer to section Managing logs